Introduction to Remote Work GHG
Policy Description
This policy supports the estimation, calculation, and tokenization of GHG emissions resulting from remote work. This policy can be used as a stand-alone methodology, or a methodology to estimate organizational Scope 3 GHG emissions from remote work to be incorporated into organizational GHG inventories in alignment with the GHG Protocol Corporate Standard and/or the GHG Protocol Scope 3 Standard. To support integration with the GHG Protocol Policies, both location and market-based emissions are calculated.
This methodology estimates electric and natural gas consumption per hour for each employee, which is refined based on the results of a detailed survey. To estimate and track GHG emissions in near-real-time, employees track, and report hours worked and GHG emissions will be estimated as hours are logged. For employees who do not respond to the survey, either default values will be used or data from respondents can be apportioned among non-respondents.
Heating and cooling energy consumption defaults were calculated based on Energy Information Administration Residential Energy Consumption Survey microdata, which was customized to specific equipment types and climate regions.
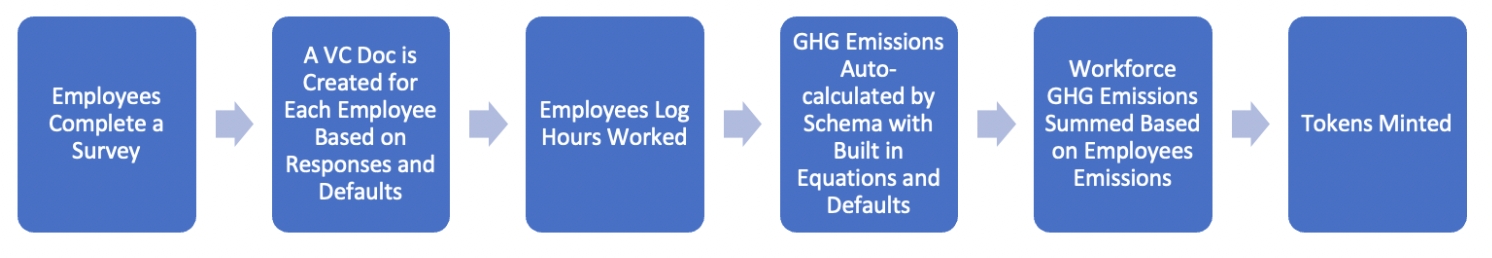
Workflow Description:
The workflow begins with each employee completing a survey to help refine their GHG estimates based on location; actual office, heating, and cooling equipment; and other important variables. Based on the responses, a verified credentials (VC) document is created. Then, employees track hours worked and GHG emissions are auto-calculated by customized schemas featuring built-in equations, defaults, and emission factors. Workforce emissions are calculated as the sum of all employee emissions and the resulting emissions are tokenized.
Last updated